Atrial fibrillation (AF) is very common in patients with RMS (rheumatic mitral stenosis). However, catheter ablation is usually not considered for treating AF in these patients due to atrial fibrosis and structural remodeling, factors that play a major role in RMS patients. The treatment of choice for these patients is the percutaneous balloon mitral commissurotomy (PBMC).
To date, evidence regarding the efficacy of percutaneous catheter AF ablation in patients undergoing PBMC (combined strategy) is scarce, with a relatively small number of patients included.
For this purpose, a recent investigation performed at Hospital Gregorio Marañón (Madrid) studied recurrences in atrial fibrillation (AF) after one year post ablation and percutaneous balloon mitral commissurotomy (PBMC) procedures in rheumatic mitral stenosis (RMS) patients.
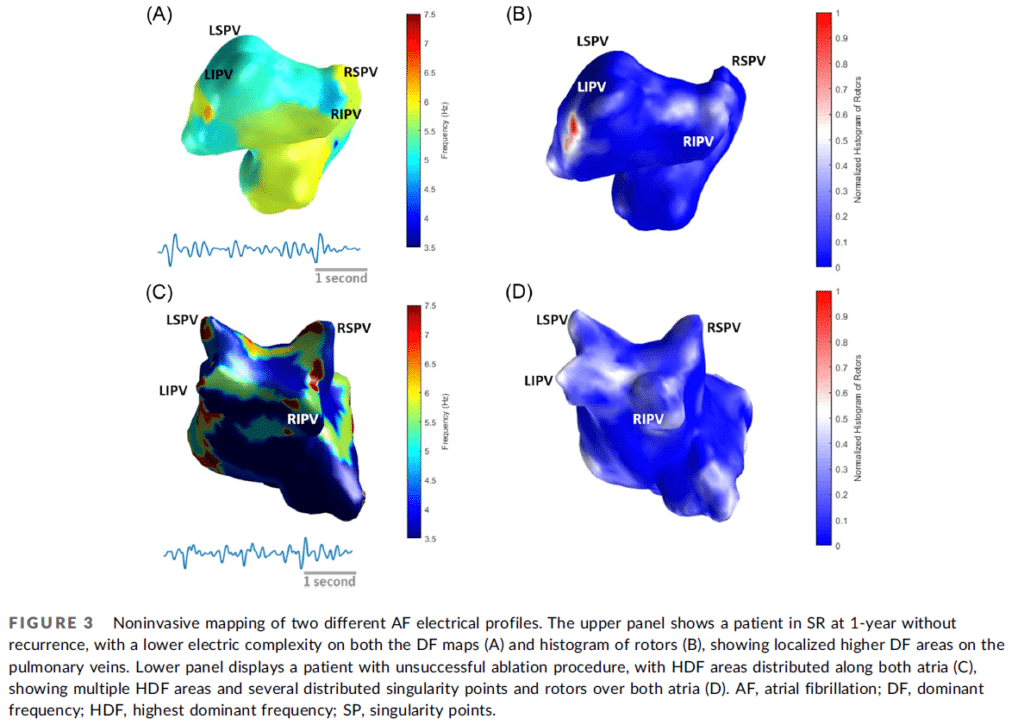
In this study, noninvasive electrocardiographic mapping (ECGi) was used for targeting triggers and maintenance sites of AF during the ablation procedure in a subset of patients. PBMC was performed during ablation in order to reduce the deleterious effects of chronic atrial stretch.
The study concludes that a combined procedure of AF ablation and PBMC significantly increased the proportion of patients in sinus rhythm at 1‐year. In this procedure, noninvasive mapping using ECGi can be a powerful tool to improve AF characterization and guide personalized AF treatment.
Díez-Delhoyo F, Sánchez De La Nava AM, Sanz-Ruiz R, Ávila P, González-Torrecilla E, Delgado-Montero A, López J, Bermejo J, Arenal Á, Atienza F, Fernández-Avilés F. Combined atrial fibrillation ablation and balloon mitral commissurotomy in patients with rheumatic mitral stenosis. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2022 Sep 28. doi: 10.1111/jce.15686. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36168873.
Available in https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/jce.15686